Recurrent images and early memories in social phobia pdf
Social anxiety disorder (social phobia) is a debilitating and common anxiety disorder, with a lifetime prevalence ranging from 6 % to 12 %. The condition has its onset in childhood and early adolescence, affects females more often than males, and if untreated is associated with high risk of
28/01/2010 · In fact, the recurrent images tend to be visualizations of aspects of memories for past socially traumatic events. That is, the images are derived from past memories. These images appear to be triggered in different social situations by cues that match the original event in some way. Like intrusive images in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), images in social phobia heighten …
conceptualization of core fear in social phobia, demonstrate how this conceptualization can be used to classify individuals with social phobia in a manner that eliminates confusion and accounts for symptom heterogeneity, and illustrate its potential utility for both
Abstract. Introduction Evidence suggests that negative self imagery plays an important role in social anxiety disorder (SAD) as a maintaining factor, and that early memories of traumatic experiences are linked to recurrent catastrophic images.
Although video feedback (VF) is shown to improve appraisals of social performance in socially anxious individuals, its impact on state anxiety during a social situation is mixed. The current study investigated the effect of combined video feedback and audience feedback (AF) on self-perceptions of performance and bodily sensations as well as
Cognitive-behavioral treatment (CBT) for social phobia is an effective treatment for many patients, but some patients do not benefit from the treatments and many remain symptomatic. Therefore, researchers have been examining techniques that may improve treatment outcome. In this paper, recent
1.1 Images in Social Anxiety According to cognitive models of social anxiety (SA), a key factor in the persistence of the disorder is the intrusion of recurrent, negative imagery into awareness when high SA
Involuntary memory Wikipedia
Frontiers The Trauma of Peer Abuse Effects of
The purpose of this pilot study is to explore whether there is a differential impact of verbal versus imagery-based cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) as a treatment augmentation strategy for individuals with social anxiety disorder (SAD).
•The anxiety, worry, or physical symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
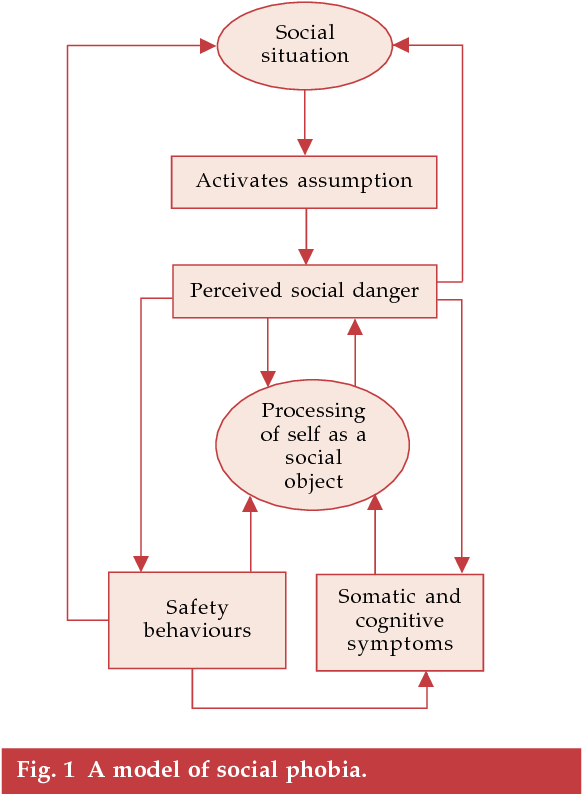
phobia attach to social events revolve around being nega- tively evaluated by other people, which in turn relates to negative self-evaluations and beliefs about the future.

Retrieval properties of negative vs. positive mental images and autobiographical memories in social anxiety: outcomes with a new measure. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 49(8), 505 – 517. DOI Behaviour Research and Therapy, 49(8), 505 – 517.
Cognitive therapy versus exposure and applied relaxation in social phobia: A randomized controlled trial.
Social situations (and their anticipation or recall) cue self-images in social anxiety disorder (4, 7), whereas binge eating and weight/shape concerns may activate images in bulimia nervosa (2, 8).
C8005 (Clinical Psychology): Social Phobia and Panic DisorderSocial Phobia and Panic Disorder Aims and Outcomes • What…
recurrent intrusive images. In this study, the . frequency with which recurrent memories were experienced on a somatic level, as panic and anxiety attacks, was not examined. Studies of burned children131 and adult survivors of natural and manmade disasters67,124 show that, over time, rucurrent symbolic or visual recollections and behavioral re-enactments abate, but there is often persistent
Negative mental imagery has been shown to be involved in the onset and maintenance of numerous clinical disorders and as a result there has been growing scientific study of the therapeutic role of positive mental imagery, with studies reporting favourable results.
Recurrent images and early memories in social phobia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38, 601-610) suggested that the images may be linked to early memories of unpleasant social experiences. This preliminary study assessed the therapeutic impact of rescripting such memories. Patients with social phobia (N=11) attended 2 sessions, 1 week apart. The first was a control session in which …
The authors proposed three stages of distorted processing that can be distinguished in social phobia: the anticipatory processing phase, the in-situation processing phase and the post-event processing phase. It is the first stage, the anticipatory processing, that is the study’s focus of attention. Clark and Wells proposed a cognitive process that takes place in social phobics before they
Recurrent images can be elicited by asking patients to recall a social situation associated with extreme anxiety. The images are usually linked to early memories. The therapist asks the patient when he or she remembers first having the experience encapsulated in the recurrent image and to recall the sensory features and meaning that these had. For example, someone who had an image of being fat
Recurrent images and early memories in social phobia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38, 601–610) suggested that the images may be linked to early memories of unpleasant social experiences. This preliminary study assessed the therapeutic impact of rescripting such memories…

images are recurrent and associated with memories of ‘traumatic’ experiences. There can be all sorts of memories which have a pictorial component and can be related to pathogenic early developed beliefs or schemas (Arntz & Weertman, 1999).
NTRODUCTION: Evidence suggests that negative self imagery plays an important role in social anxiety disorder (SAD) as a maintaining factor, and that early memories of traumatic experiences are linked to recurrent catastrophic images. Previous research has showed that cognitive restructuring combined
Taken together, the results suggest that in patients with social phobia, early unpleasant experiences may lead to the development of excessively negative images of their social selves that are
Imagery and core beliefs in fear of vomiting Research
Aims: This study aimed to provide an in-depth analysis of the phenomenology of negative imagery experienced by socially anxious individuals, and to compare recurrent and intrusive images with images deliberately generated by participants during the study.
Anxiety is related to recurrent obsessive thoughts, images, or impulses. Symptoms may also be tied to compulsive behavior in the form of regimented, rigid …
Cognitive therapy versus exposure and applied relaxation in social phobia: A randomized controlled trial. DM Clark, A Ehlers, A Hackmann, F McManus, M Fennell, N Grey, Journal of consulting and clinical psychology 74 (3), 568 , 2006
Social anxiety disorder (SAD) is a common, distressing and persistent mental illness. Recent studies have identified a number of psychological factors that could explain the maintenance of the disorder.
social phobia one client may fear sweating while another may be concerned that their voice wavers and that they sound boring), the meaning of the images are related to their feared predictions and are broadly consistent within a given disorder (5) (6) (7)
Experimental studies of components in the treatment for social anxiety disorder Nilsson, Jan-Erik LU Mark; Abstract Social anxiety disorder (social phobia) is a debilitating and common anxiety disorder, with a lifetime prevalence ranging from 6 % to 12 %.
Comments . Good topic choice, very relevant to a lot of people. Good amount of information on your page, however would it be beneficial to dive into different reasons for social anxiety eg bullying, domestic violence etc? – export pdf from powerpoint when images are larger than slides van Hout, W., & Bouman, T. (2016). Imagery and core beliefs in fear of vomiting. 8th World Congress of Behavioural and Cognitive Therapies , Melbourne, Australia. title = “Imagery and core beliefs in fear of vomiting”, abstract = “Aim The main aim of the present study was to get insight into the
An ability to elicit the images or impressions that form client’s self-image in social situations (i.e. how they think they appear to others) An ability to identify socially traumatic early …
A diagnosis of social anxiety disorder did not affect the reactions to social exclusion on any measure.Conclusions: Findings indicate that stress reactions to social exclusion depend more on previous experiences of peer victimization than on a diagnosis of social anxiety disorder. The findings indicate that memories of negative social experiences can determine the initial stress reaction to
The results suggested that in patients with social phobia, early unpleasant experiences may lead to the development of excessively negative images of their social selves that are repeatedly activated in subsequent social situations and fail to
1.1 Social Anxiety Disorder. Social anxiety disorder (SAD, also known as social phobia) is a highly prevalent and often debilitating condition characterized by fear of negative evaluation and high levels of anxiety and avoidance when engaged in social or performance situations (Jefferys, 1997).
Rescripting Early Memories Linked to Negative Images in Social Phobia: A Pilot Study Jennifer Wild, Institute of Psychiatry at King’s College London
PDF Abstract. Abstract. Imagery rescripting (ImRS) effectively targets intrusive images and symptoms in a number of disorders, but the mechanisms of change behind it are not yet clear. This study investigated the impact of ImRS on the characteristics of adverse self-defining memories and post-recall working selves in a non-clinical sample. In the first session, participants recalled an adverse
Involuntary memory, also known as involuntary explicit memory, involuntary conscious memory, involuntary aware memory, and most commonly, involuntary autobiographical memory, is a subcomponent of memory that occurs when cues encountered in everyday life evoke recollections of the past without conscious effort.
Cognitive theories of social anxiety propose that negative mental imagery plays a central role in the maintenance of the disorder. Research has indicated that the content of such mental imagery represents negative core beliefs and derives from specific formative, negative autobiographical events.
that their negative self-images were recurrent and associated with memories of traumatic early social experiences (Hackmann, Clark, & McManus, 2000). Negative self-image has adverse effects on individuals with social phobia inmany ways.First, holdinga negative imagein mind increases anxiety, self-focused attention, and safety behaviors, and thus undermines effective social performance …
Recurrent and persistent thoughts, impulses, or images that are intrusive and unwanted that cause anxiety or stress Person attempts to ignore or suppress these thoughts with some other thought or action (compulsion)
Vernachlässigte Folgen sozialer Traumatisierung Trauma
The purpose of this research was to examine earliest memories in patients with a mental disorder and their clinical relevance to diagnosis and treatment. Method: A semi-structured early memory questionnaire was developed and 50 patients with anxiety, depression or a …
Recurrent images and early memories accurate reflection of how they appear to other in social phobia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38, people. They therefore think they come across 601–610) suggested that the images may be linked to early much worse than they actually do, which tends to memories of unpleasant social experiences. This preliminary maintain their social anxiety. Second, …
Read “The efficacy of imagery rescripting compared to cognitive restructuring for social anxiety disorder, Journal Of Anxiety Disorders” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips.
Negative self-images appear to play a role in the maintenance of social phobia and research suggests they are often linked to earlier memories of socially traumatic events.
These images are usually distorted, generally encapsulate negative meanings about the self, and are often linked to aversive early memories such as being bullied (Hackmann, Clark, & McManus, 2000 Hackmann, A., Clark, D. M. and McManus, F. 2000.
Social Anxiety and the Effects of Engaging Springer
Single-Session Imagery Rescripting for Social Anxiety
Early memories Clinical relevance and

Anxiety disorders thelancet.com
Pathology Final (Anxiety) Flashcards Quizlet


Impact of imagery rescripting on adverse self-defining
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guided_imagery
Cognitive-behavioral treatment of social phobia New
gareth morgan images of organization pdf – Medical Psych – Clinical Psychology – Social Phobia and
Imagery-based CBT for Social Anxiety Disorder Piloting a

Specificity of cognitive biases in social phobia and their
ANXIETY DISORDERS FMF
Experimental studies of components in the treatment for
Mental imagery in anxiety disorders Colette R. Hirsch
Recurrent images and early memories accurate reflection of how they appear to other in social phobia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38, people. They therefore think they come across 601–610) suggested that the images may be linked to early much worse than they actually do, which tends to memories of unpleasant social experiences. This preliminary maintain their social anxiety. Second, …
•The anxiety, worry, or physical symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
Cognitive therapy versus exposure and applied relaxation in social phobia: A randomized controlled trial.
1.1 Social Anxiety Disorder. Social anxiety disorder (SAD, also known as social phobia) is a highly prevalent and often debilitating condition characterized by fear of negative evaluation and high levels of anxiety and avoidance when engaged in social or performance situations (Jefferys, 1997).
Abstract. Introduction Evidence suggests that negative self imagery plays an important role in social anxiety disorder (SAD) as a maintaining factor, and that early memories of traumatic experiences are linked to recurrent catastrophic images.
NTRODUCTION: Evidence suggests that negative self imagery plays an important role in social anxiety disorder (SAD) as a maintaining factor, and that early memories of traumatic experiences are linked to recurrent catastrophic images. Previous research has showed that cognitive restructuring combined
The purpose of this pilot study is to explore whether there is a differential impact of verbal versus imagery-based cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) as a treatment augmentation strategy for individuals with social anxiety disorder (SAD).
phobia attach to social events revolve around being nega- tively evaluated by other people, which in turn relates to negative self-evaluations and beliefs about the future.
APT-2003-Veale-258-64 Social Anxiety Disorder Phobia
Medical Psych – Clinical Psychology – Social Phobia and
phobia attach to social events revolve around being nega- tively evaluated by other people, which in turn relates to negative self-evaluations and beliefs about the future.
that their negative self-images were recurrent and associated with memories of traumatic early social experiences (Hackmann, Clark, & McManus, 2000). Negative self-image has adverse effects on individuals with social phobia inmany ways.First, holdinga negative imagein mind increases anxiety, self-focused attention, and safety behaviors, and thus undermines effective social performance …
Cognitive therapy versus exposure and applied relaxation in social phobia: A randomized controlled trial.
The purpose of this pilot study is to explore whether there is a differential impact of verbal versus imagery-based cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) as a treatment augmentation strategy for individuals with social anxiety disorder (SAD).
Recurrent images and early memories in social phobia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38, 601–610) suggested that the images may be linked to early memories of unpleasant social experiences. This preliminary study assessed the therapeutic impact of rescripting such memories…
The results suggested that in patients with social phobia, early unpleasant experiences may lead to the development of excessively negative images of their social selves that are repeatedly activated in subsequent social situations and fail to
Cognitive-behavioral treatment (CBT) for social phobia is an effective treatment for many patients, but some patients do not benefit from the treatments and many remain symptomatic. Therefore, researchers have been examining techniques that may improve treatment outcome. In this paper, recent
Rescripting Early Memories Linked to Negative Images in Social Phobia: A Pilot Study Jennifer Wild, Institute of Psychiatry at King’s College London
Negative mental imagery has been shown to be involved in the onset and maintenance of numerous clinical disorders and as a result there has been growing scientific study of the therapeutic role of positive mental imagery, with studies reporting favourable results.
conceptualization of core fear in social phobia, demonstrate how this conceptualization can be used to classify individuals with social phobia in a manner that eliminates confusion and accounts for symptom heterogeneity, and illustrate its potential utility for both
Comments . Good topic choice, very relevant to a lot of people. Good amount of information on your page, however would it be beneficial to dive into different reasons for social anxiety eg bullying, domestic violence etc?
social phobia one client may fear sweating while another may be concerned that their voice wavers and that they sound boring), the meaning of the images are related to their feared predictions and are broadly consistent within a given disorder (5) (6) (7)
•The anxiety, worry, or physical symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
Ann Hackmann Academia.edu
Memories in public speaking performance anxiety
28/01/2010 · In fact, the recurrent images tend to be visualizations of aspects of memories for past socially traumatic events. That is, the images are derived from past memories. These images appear to be triggered in different social situations by cues that match the original event in some way. Like intrusive images in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), images in social phobia heighten …
Cognitive-behavioral treatment (CBT) for social phobia is an effective treatment for many patients, but some patients do not benefit from the treatments and many remain symptomatic. Therefore, researchers have been examining techniques that may improve treatment outcome. In this paper, recent
recurrent intrusive images. In this study, the . frequency with which recurrent memories were experienced on a somatic level, as panic and anxiety attacks, was not examined. Studies of burned children131 and adult survivors of natural and manmade disasters67,124 show that, over time, rucurrent symbolic or visual recollections and behavioral re-enactments abate, but there is often persistent
Involuntary memory, also known as involuntary explicit memory, involuntary conscious memory, involuntary aware memory, and most commonly, involuntary autobiographical memory, is a subcomponent of memory that occurs when cues encountered in everyday life evoke recollections of the past without conscious effort.
Negative mental imagery has been shown to be involved in the onset and maintenance of numerous clinical disorders and as a result there has been growing scientific study of the therapeutic role of positive mental imagery, with studies reporting favourable results.
Recurrent images and early memories in social phobia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38, 601–610) suggested that the images may be linked to early memories of unpleasant social experiences. This preliminary study assessed the therapeutic impact of rescripting such memories…
Cognitive therapy versus exposure and applied relaxation in social phobia: A randomized controlled trial.
1.1 Images in Social Anxiety According to cognitive models of social anxiety (SA), a key factor in the persistence of the disorder is the intrusion of recurrent, negative imagery into awareness when high SA
phobia attach to social events revolve around being nega- tively evaluated by other people, which in turn relates to negative self-evaluations and beliefs about the future.
The results suggested that in patients with social phobia, early unpleasant experiences may lead to the development of excessively negative images of their social selves that are repeatedly activated in subsequent social situations and fail to
social phobia one client may fear sweating while another may be concerned that their voice wavers and that they sound boring), the meaning of the images are related to their feared predictions and are broadly consistent within a given disorder (5) (6) (7)
Experimental studies of components in the treatment for social anxiety disorder Nilsson, Jan-Erik LU Mark; Abstract Social anxiety disorder (social phobia) is a debilitating and common anxiety disorder, with a lifetime prevalence ranging from 6 % to 12 %.
Recurrent and persistent thoughts, impulses, or images that are intrusive and unwanted that cause anxiety or stress Person attempts to ignore or suppress these thoughts with some other thought or action (compulsion)
The purpose of this pilot study is to explore whether there is a differential impact of verbal versus imagery-based cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) as a treatment augmentation strategy for individuals with social anxiety disorder (SAD).
Comments . Good topic choice, very relevant to a lot of people. Good amount of information on your page, however would it be beneficial to dive into different reasons for social anxiety eg bullying, domestic violence etc?
Intrusive Mental Imagery in Psychological Disorders Is
Ann Hackmann Academia.edu
Aims: This study aimed to provide an in-depth analysis of the phenomenology of negative imagery experienced by socially anxious individuals, and to compare recurrent and intrusive images with images deliberately generated by participants during the study.
28/01/2010 · In fact, the recurrent images tend to be visualizations of aspects of memories for past socially traumatic events. That is, the images are derived from past memories. These images appear to be triggered in different social situations by cues that match the original event in some way. Like intrusive images in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), images in social phobia heighten …
recurrent intrusive images. In this study, the . frequency with which recurrent memories were experienced on a somatic level, as panic and anxiety attacks, was not examined. Studies of burned children131 and adult survivors of natural and manmade disasters67,124 show that, over time, rucurrent symbolic or visual recollections and behavioral re-enactments abate, but there is often persistent
Rescripting Early Memories Linked to Negative Images in Social Phobia: A Pilot Study Jennifer Wild, Institute of Psychiatry at King’s College London
Recurrent images and early memories accurate reflection of how they appear to other in social phobia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38, people. They therefore think they come across 601–610) suggested that the images may be linked to early much worse than they actually do, which tends to memories of unpleasant social experiences. This preliminary maintain their social anxiety. Second, …
An ability to elicit the images or impressions that form client’s self-image in social situations (i.e. how they think they appear to others) An ability to identify socially traumatic early …
Memories in public speaking performance anxiety
Frontiers The Trauma of Peer Abuse Effects of
Abstract. Introduction Evidence suggests that negative self imagery plays an important role in social anxiety disorder (SAD) as a maintaining factor, and that early memories of traumatic experiences are linked to recurrent catastrophic images.
Recurrent images and early memories in social phobia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38, 601–610) suggested that the images may be linked to early memories of unpleasant social experiences. This preliminary study assessed the therapeutic impact of rescripting such memories…
The results suggested that in patients with social phobia, early unpleasant experiences may lead to the development of excessively negative images of their social selves that are repeatedly activated in subsequent social situations and fail to
Cognitive theories of social anxiety propose that negative mental imagery plays a central role in the maintenance of the disorder. Research has indicated that the content of such mental imagery represents negative core beliefs and derives from specific formative, negative autobiographical events.
The purpose of this research was to examine earliest memories in patients with a mental disorder and their clinical relevance to diagnosis and treatment. Method: A semi-structured early memory questionnaire was developed and 50 patients with anxiety, depression or a …
Cognitive theories of social anxiety propose that negative mental imagery plays a central role in the maintenance of the disorder. Research has indicated that the content of such mental imagery represents negative core beliefs and derives from specific formative, negative autobiographical events.
Cognitive Factors that Maintain Social Anxiety Disorder a
Single-Session Imagery Rescripting for Social Anxiety
Specificity of cognitive biases in social phobia and their
28/01/2010 · In fact, the recurrent images tend to be visualizations of aspects of memories for past socially traumatic events. That is, the images are derived from past memories. These images appear to be triggered in different social situations by cues that match the original event in some way. Like intrusive images in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), images in social phobia heighten …
social phobia Clark and Wells model
Vernachlässigte Folgen sozialer Traumatisierung Trauma
Involuntary memory Wikipedia
Comments . Good topic choice, very relevant to a lot of people. Good amount of information on your page, however would it be beneficial to dive into different reasons for social anxiety eg bullying, domestic violence etc?
Early memories Clinical relevance and
Specificity of cognitive biases in social phobia and their
Single-Session Imagery Rescripting for Social Anxiety Disorder
The purpose of this pilot study is to explore whether there is a differential impact of verbal versus imagery-based cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) as a treatment augmentation strategy for individuals with social anxiety disorder (SAD).
Anxiety & Children OregonCounseling
Vernachlässigte Folgen sozialer Traumatisierung Trauma
Specificity of cognitive biases in social phobia and their
Involuntary memory, also known as involuntary explicit memory, involuntary conscious memory, involuntary aware memory, and most commonly, involuntary autobiographical memory, is a subcomponent of memory that occurs when cues encountered in everyday life evoke recollections of the past without conscious effort.
Imagery and core beliefs in fear of vomiting Research