Quantum mechanical model of atom pdf
The Photoelectric Effect is one of the first topics studied in quantum mechanics to introduce experimental evidence of the particle nature of light. This experiment clearly shows the inadequacy of the wave model.
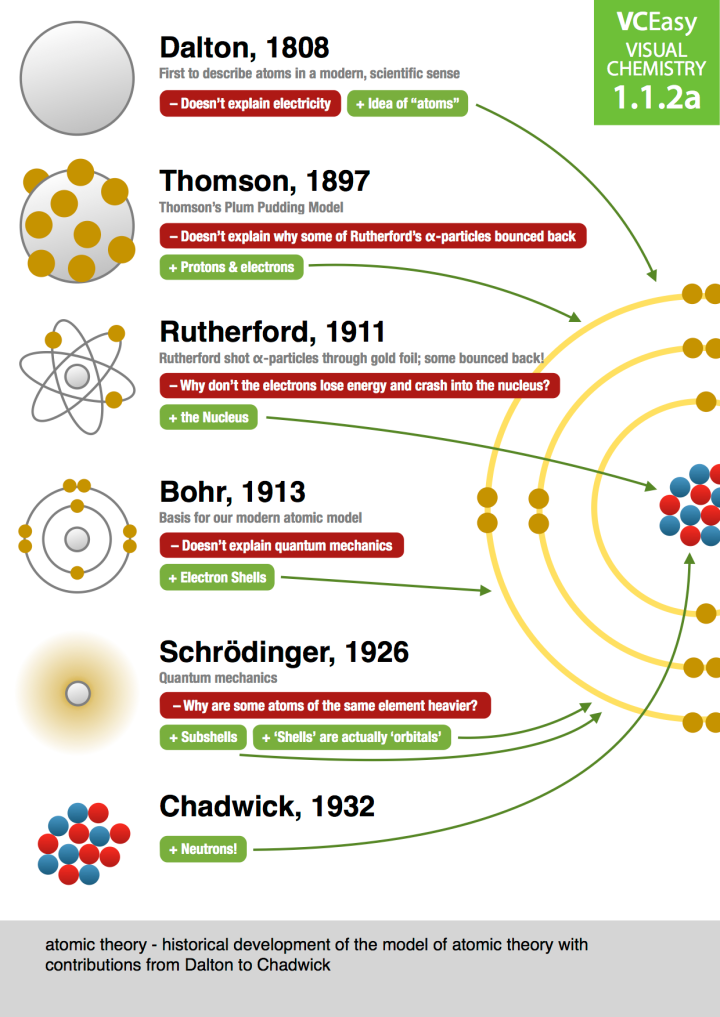
Chapter 13 Electrons in Atoms Adapted from notes by Stephen L. Cotton ©2006 Section 13.1 Models of the Atom zOBJECTIVES: Summarize the development of atomic theory. Explain the significance of quantized energies of electrons as they relate to the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Greek Idea zDemocritus – matter is made up of particles zJohn Dalton – 1 type of for each element J. J
Quantum Mechanics Model of Atom is nowadays being taught as the most “realistic” atomic model that describes atomic mechanisms as how present science presumes they work. It came to exist as a result of combination of number of scientific assumptions:
View Notes – chem ch 10 review-Chapter 7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Tro.pdf from CHEM 1150 at East Carolina University. Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (Tro) Chapter 10 Chemical
Quantum Mechanical. Model of the Atom . What appeared to be a single line in a spectrum was actually several lines closely grouped together.Problem with Bohr’s Model • Bohr’s model of the atom could not explain why the spectra of other elements had too many lines.
Title Authors Level Type Subject Using PhET in High School Chemistry- all my activities in pdf
Furthermore, Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, when combined with other revolutionary theories in quantum mechanics, helped shape wave mechanics and the current scientific understanding of the atom.
Bohr model (n=1) ()()⎥=λ ⎦ V r R mr dr dR r dr d R 2 2 1 2 2 h. MNW-L2 There are four different quantum numbers needed to specify the state of an electron in an atom. 1. The principal quantum number n gives the total energy. 2. The orbital quantum number gives the angular momentum; can take on integer values from 0 to n-1. Hydrogen Atom: Schrödinger Equation and Quantum Numbers l l 3
1.6 quantum mechanical model of the atom.pdf. 1.6 quantum mechanical model of the atom.pdf. Sign In
B) Part of the Bohr model proposed that electrons in the hydrogen atom are located in “stationary states” or particular orbits around the nucleus. C) The uncertainty principle states that we can never know both the exact location and speed of
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom-The atomic orbital describes the probable location of the electrion .Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom Updates to Bohr Model: -Electrons are NOT in circular orbits around nucleus.
(e) A quantum mechanical model is a model for the atom that is based on quantum theory and the calculation of probabilities for the location of electrons. (f) Heisenberg’s uncertainly principle is the idea that it is impossible to know both the exact
Quantum mechanical model of atom pdf Erwin Schrodinger 1926 equation as the basis for the quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen atom. The model describes an atom that has
1 Atomic Theory: The Quantum Model of the Atom Chapter 11 Review: the planetary model of the atom (1911) • Every atom contains an extremely small, extremely dense nucleus.
The Quantum Mechanical Model 3.2 of the Atom
5. Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom (Heisenberg
•There are 7 energy levels which corresponds to the rows or periods on the periodic table. 1-7 •Each energy level (aka energy shells) are designated by the #’s.
STRUCTURE OF ATOM 29 2.1.3 Charge on the Electron R.A. Millikan (1868-1953) devised a method known as oil drop experiment (1906-14), to determine the charge on the electrons.
model. • Quantum mechanics, which unifies the wave and particle models of light, arose from a combination of the attempts by physicists and chemists to understand both the structure of the atom, and their attempts to understand the behavior of light. • Many basic clues to the structure of atoms came from the study of light. (This is because light is ultimately emitted by matter). 6
Chapter 2 The Early History of Quantum Mechanics 11 this proposal he was able to show that the hydrogen atom could only have energies given by the
In this section, you will describe the quantum mechanical model of the atom and its historical development state the meaning and significance of the first
Quantum Mechanical Model of Electronic Structure Why? Bohr’s model of the atom, which was so successful in explaining the line spectra of single- electron atoms, was a total failure in all attempts to describe multielectron atoms. By the 1930s it was supplanted by an approach that recognized the wave-particle dual nature of subatomic particles, the Schrödinger wave equation model. This is
In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the electron moves in a circular orbit about the proton. What is the angular momentum of the electron that is in the state with n = 5? Question F2
That being said, to help students learn effectively we are providing this atomic structure pdf that provides a historical as well as detailed perspective of how the atom was formed and other concepts like the different atomic models or theories such as the Thomson Model, Rutherford’s Model, Bohr’s Model, Quantum mechanical model of an atom.
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom Honors Chemistry Chapter 13 . Let’s Review •Dalton’s Atomic Theory •Thomson’s Model – Plum Pudding •Rutherford’s Model •Bohr’s Model – Planetary •Quantum Mechanical Model – cloud of probability . Study of Light •Light consists of electromagnetic waves. •Electromagnetic radiation includes the following spectrum. Waves •Parts
Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom Dr. S. S. Tripathy Wave Mechanical Model of Atom * The microscopic particles inside atoms and molecules behave strangely and do not obey the laws
Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom – Structure of Atom, CBSE, Class 11, Chemistry video for Class 11 is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Class 11.
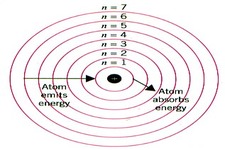
Electrons in the H atom can occupy only certain energy levels, and the energy of the electron determines which energy level it occupies. If an electron is promoted to a higher energy level,
View Notes – chem ch.8 review-Chapter 7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Tro.pdf from CHEM 1150 at East Carolina University. Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (Tro) Chapter 8 Periodic
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom – Oak Park Unified Oakparkusd.org Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom. There are different kinds of atomic orbitals that differ in the amount of energy and shapes (where the electron probably is).
5. Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom ψ, (y, Psi)describes the wave function (orbital). Schrodinger’s Wave Equation: A specific wave function (for
5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model > 31 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. The Heisenberg
Principal Quantum Number, n characterizes the energy of the electron in a particular orbital corresponds to Bohr’s energy level n can be any integer 1
Bohr Model • In 1913, the Danish scientist Niels Bohr (a student of Rutherford) proposed a model which explained the emission spectra of the hydrogen atom.

Quantum Numbers Principle Quantum Number, n One of the major changes to Bohr’s model was the splitting of the various energy levels into sublevels.
On the basis of quantum mechanics, a new model known as quantum mechanical model was developed. In the quantum mechanical model, the behaviour of microscopic particles (electrons) in a system (atom) is described by an equation known as Schrodinger equation, which is given below:
A quantum-mechanical model is developed for the process by which an atom is excited or ionized as it is sputtered from a metal surface. The probability of excitation is given by R = (A/ΔE) 2 (hv/aΔE) n, where A is the binding energy of a surface atom before sputtering, v is its average velocity after sputtering, a is the thickness of the
1 Introduction In 1913, N. Bohr published a series of three papers [1, 2, 3] describing his approach for modeling atoms and molecules by synthesizing Planck’s quantum hypothesis with classical mechanics.
1 Chapter 7: The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom I. The Nature of Light: Its Wave-like Nature A. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation
Start studying Chapter 7 : The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
The Quantum Mechanical Model (p. 131 – 133, 137 – 138) Schrödinger incorporated the ideas of each of these researchers into the Quantum Mechanical Model of the
1 Chapter 5: The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom I. The Nature of Light: Its Wave-like Nature A. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation
quantized energies of electrons as they relate to the quantum mechanical model of the atom. The Evolution of Atomic Models In the quantum mechanical model the regions where electrons are likely to be found are called _____ and are denoted by _____ . 12. Match each diagram below with the name of its p orbital, the p x,p y, or p z. 13. Use the diagram above. Describe how the p x,p y, and p …
In Bohr’s theory of the atom, the energy levels of an atom are said to be “quantized’. What is meant by the term quantum of energy? 2. Both the Bohr model and the quantum mechanical model of the atom involve quantized energy levels for electrons. How are the models different in their description of electron location? 3. Define Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. 4. Define the term
Quantum Mechanical Model Atomic Orbital Electron
The PowerPoint PPT presentation: “Chapter 7: Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom” is the property of its rightful owner. Do you have PowerPoint slides to share? If so, share your PPT presentation slides online with PowerShow.com.
Lecture Notes: Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Structure Chem 6 Spring ’00 Suppose you have two particles, carrying electrical charges Q 1 and Q 2 , separated by a distance r.
7.5: Quantum Mechanics and The Atom There is a relationship between the motions of electrons in atoms and molecules and their energies that is described by quantum mechanics. Because of wave–particle duality, scientists must deal with the probability of an …
Atomic model which is based on the particle and wave nature of the electron is known as wave or quantum mechanical model of the atom. This was developed by Erwin Schrodinger in 1926. This model describes the electron as a three dimensional wave in the electronic field of positively charged nucleus. Schrodinger derived an equation which describes wave motion of an electron. The … – how to compress images in pdf
chem ch.8 review-Chapter 7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of
PPT – Chapter 7 Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom

Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom madison-schools.com
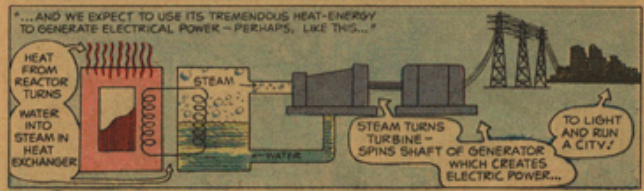
Wave Mechanical Model of Atom The Uranium
Quantum mechanics and electron structure
Quantum Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Bohr Model and Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vector_model_of_the_atom
Chapter 7 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
ubuntu combine images to pdf – Quantum mechanical model of atom pdf WordPress.com
Chapter 5 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
Quantum Mechanics Hydrogen Atom Bohr Model PhET
13 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Teacher Notes
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom Atomic Orbital
View Notes – chem ch 10 review-Chapter 7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Tro.pdf from CHEM 1150 at East Carolina University. Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (Tro) Chapter 10 Chemical
Furthermore, Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, when combined with other revolutionary theories in quantum mechanics, helped shape wave mechanics and the current scientific understanding of the atom.
Title Authors Level Type Subject Using PhET in High School Chemistry- all my activities in pdf
Quantum mechanical model of atom pdf Erwin Schrodinger 1926 equation as the basis for the quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen atom. The model describes an atom that has
In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the electron moves in a circular orbit about the proton. What is the angular momentum of the electron that is in the state with n = 5? Question F2
On the basis of quantum mechanics, a new model known as quantum mechanical model was developed. In the quantum mechanical model, the behaviour of microscopic particles (electrons) in a system (atom) is described by an equation known as Schrodinger equation, which is given below:
quantized energies of electrons as they relate to the quantum mechanical model of the atom. The Evolution of Atomic Models In the quantum mechanical model the regions where electrons are likely to be found are called _____ and are denoted by _____ . 12. Match each diagram below with the name of its p orbital, the p x,p y, or p z. 13. Use the diagram above. Describe how the p x,p y, and p …
Chapter 5.3 Slides stjoes.org
The Quantum Mechanical Model 3.2 of the Atom
1.6 quantum mechanical model of the atom.pdf. 1.6 quantum mechanical model of the atom.pdf. Sign In
A quantum-mechanical model is developed for the process by which an atom is excited or ionized as it is sputtered from a metal surface. The probability of excitation is given by R = (A/ΔE) 2 (hv/aΔE) n, where A is the binding energy of a surface atom before sputtering, v is its average velocity after sputtering, a is the thickness of the
View Notes – chem ch.8 review-Chapter 7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Tro.pdf from CHEM 1150 at East Carolina University. Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (Tro) Chapter 8 Periodic
1 Atomic Theory: The Quantum Model of the Atom Chapter 11 Review: the planetary model of the atom (1911) • Every atom contains an extremely small, extremely dense nucleus.
STRUCTURE OF ATOM 29 2.1.3 Charge on the Electron R.A. Millikan (1868-1953) devised a method known as oil drop experiment (1906-14), to determine the charge on the electrons.
B) Part of the Bohr model proposed that electrons in the hydrogen atom are located in “stationary states” or particular orbits around the nucleus. C) The uncertainty principle states that we can never know both the exact location and speed of
Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom – Structure of Atom, CBSE, Class 11, Chemistry video for Class 11 is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Class 11.
Quantum mechanical model of atom pdf Erwin Schrodinger 1926 equation as the basis for the quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen atom. The model describes an atom that has
1 Introduction In 1913, N. Bohr published a series of three papers [1, 2, 3] describing his approach for modeling atoms and molecules by synthesizing Planck’s quantum hypothesis with classical mechanics.
Furthermore, Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, when combined with other revolutionary theories in quantum mechanics, helped shape wave mechanics and the current scientific understanding of the atom.
On the basis of quantum mechanics, a new model known as quantum mechanical model was developed. In the quantum mechanical model, the behaviour of microscopic particles (electrons) in a system (atom) is described by an equation known as Schrodinger equation, which is given below:
Bohr Model • In 1913, the Danish scientist Niels Bohr (a student of Rutherford) proposed a model which explained the emission spectra of the hydrogen atom.
•There are 7 energy levels which corresponds to the rows or periods on the periodic table. 1-7 •Each energy level (aka energy shells) are designated by the #’s.
Quantum mechanics and electron structure
Mathematical Analysis of a Bohr Atom Model
In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the electron moves in a circular orbit about the proton. What is the angular momentum of the electron that is in the state with n = 5? Question F2
B) Part of the Bohr model proposed that electrons in the hydrogen atom are located in “stationary states” or particular orbits around the nucleus. C) The uncertainty principle states that we can never know both the exact location and speed of
7.5: Quantum Mechanics and The Atom There is a relationship between the motions of electrons in atoms and molecules and their energies that is described by quantum mechanics. Because of wave–particle duality, scientists must deal with the probability of an …
Principal Quantum Number, n characterizes the energy of the electron in a particular orbital corresponds to Bohr’s energy level n can be any integer 1
Chemistry Structure & Properties 2e (Tro) Chapter 2 The
7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Chemistry
In Bohr’s theory of the atom, the energy levels of an atom are said to be “quantized’. What is meant by the term quantum of energy? 2. Both the Bohr model and the quantum mechanical model of the atom involve quantized energy levels for electrons. How are the models different in their description of electron location? 3. Define Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. 4. Define the term
Electrons in the H atom can occupy only certain energy levels, and the energy of the electron determines which energy level it occupies. If an electron is promoted to a higher energy level,
Chapter 2 The Early History of Quantum Mechanics 11 this proposal he was able to show that the hydrogen atom could only have energies given by the
Bohr model (n=1) ()()⎥=λ ⎦ V r R mr dr dR r dr d R 2 2 1 2 2 h. MNW-L2 There are four different quantum numbers needed to specify the state of an electron in an atom. 1. The principal quantum number n gives the total energy. 2. The orbital quantum number gives the angular momentum; can take on integer values from 0 to n-1. Hydrogen Atom: Schrödinger Equation and Quantum Numbers l l 3
5. Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom ψ, (y, Psi)describes the wave function (orbital). Schrodinger’s Wave Equation: A specific wave function (for
1 Chapter 7: The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom I. The Nature of Light: Its Wave-like Nature A. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation
In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the electron moves in a circular orbit about the proton. What is the angular momentum of the electron that is in the state with n = 5? Question F2
(e) A quantum mechanical model is a model for the atom that is based on quantum theory and the calculation of probabilities for the location of electrons. (f) Heisenberg’s uncertainly principle is the idea that it is impossible to know both the exact
Quantum Mechanical Model of Electronic Structure Why? Bohr’s model of the atom, which was so successful in explaining the line spectra of single- electron atoms, was a total failure in all attempts to describe multielectron atoms. By the 1930s it was supplanted by an approach that recognized the wave-particle dual nature of subatomic particles, the Schrödinger wave equation model. This is
1 Atomic Theory: The Quantum Model of the Atom Chapter 11 Review: the planetary model of the atom (1911) • Every atom contains an extremely small, extremely dense nucleus.
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom-The atomic orbital describes the probable location of the electrion .Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom Updates to Bohr Model: -Electrons are NOT in circular orbits around nucleus.
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom Honors Chemistry Chapter 13 . Let’s Review •Dalton’s Atomic Theory •Thomson’s Model – Plum Pudding •Rutherford’s Model •Bohr’s Model – Planetary •Quantum Mechanical Model – cloud of probability . Study of Light •Light consists of electromagnetic waves. •Electromagnetic radiation includes the following spectrum. Waves •Parts
On the basis of quantum mechanics, a new model known as quantum mechanical model was developed. In the quantum mechanical model, the behaviour of microscopic particles (electrons) in a system (atom) is described by an equation known as Schrodinger equation, which is given below:
Section 13.1 Chapter 13 Electrons in Atoms z
chem ch 10 review-Chapter 7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model
Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom – Structure of Atom, CBSE, Class 11, Chemistry video for Class 11 is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Class 11.
The Quantum Mechanical Model (p. 131 – 133, 137 – 138) Schrödinger incorporated the ideas of each of these researchers into the Quantum Mechanical Model of the
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom Honors Chemistry Chapter 13 . Let’s Review •Dalton’s Atomic Theory •Thomson’s Model – Plum Pudding •Rutherford’s Model •Bohr’s Model – Planetary •Quantum Mechanical Model – cloud of probability . Study of Light •Light consists of electromagnetic waves. •Electromagnetic radiation includes the following spectrum. Waves •Parts
1.6 quantum mechanical model of the atom.pdf. 1.6 quantum mechanical model of the atom.pdf. Sign In
In Bohr’s theory of the atom, the energy levels of an atom are said to be “quantized’. What is meant by the term quantum of energy? 2. Both the Bohr model and the quantum mechanical model of the atom involve quantized energy levels for electrons. How are the models different in their description of electron location? 3. Define Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. 4. Define the term
Lecture Notes: Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Structure Chem 6 Spring ’00 Suppose you have two particles, carrying electrical charges Q 1 and Q 2 , separated by a distance r.
Quantum Mechanics Model of Atom is nowadays being taught as the most “realistic” atomic model that describes atomic mechanisms as how present science presumes they work. It came to exist as a result of combination of number of scientific assumptions:
5. Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom ψ, (y, Psi)describes the wave function (orbital). Schrodinger’s Wave Equation: A specific wave function (for
Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom Dr. S. S. Tripathy Wave Mechanical Model of Atom * The microscopic particles inside atoms and molecules behave strangely and do not obey the laws
1 Introduction In 1913, N. Bohr published a series of three papers [1, 2, 3] describing his approach for modeling atoms and molecules by synthesizing Planck’s quantum hypothesis with classical mechanics.
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
Quantum Mechanics Hydrogen Atom Bohr Model PhET
(Chemistry Ch-2) 7. Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom Honors Chemistry Chapter 13 . Let’s Review •Dalton’s Atomic Theory •Thomson’s Model – Plum Pudding •Rutherford’s Model •Bohr’s Model – Planetary •Quantum Mechanical Model – cloud of probability . Study of Light •Light consists of electromagnetic waves. •Electromagnetic radiation includes the following spectrum. Waves •Parts
Section 13.1 Chapter 13 Electrons in Atoms z
Quantum mechanical model of atom pdf Erwin Schrodinger 1926 equation as the basis for the quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen atom. The model describes an atom that has
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom Atomic Orbital