Quantum mechanical description of the atom pdf
7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Anyone who is not shocked by quantum mechanics has not understood it. —Neils Bohr (1885–1962) 7.1 Schrödinger’s Cat 253 7.2 The Nature of Light 254 7.3 Atomic Spectroscopy and the Bohr Model 262 7.4 The Wave Nature of Matter: the de Broglie Wavelength, the Uncertainty Principle, and Indeterminacy 264 7.5 Quantum Mechanics and the Atom …
Quantum Mechanics; Hydrogen Atom; Bohr Model; DeBroglie Wavelength; Schrodinger Model; Description How did scientists figure out the structure of atoms without looking at them? Try out different models by shooting light at the atom. Check how the prediction of the model matches the experimental results. Sample Learning Goals Visualize different models of the hydrogen atom. …
Quantum mechanics is a linear theory, and so it is natural that vector spaces play an important role in it. A physical A physical state is represented mathematically by a vector in a Hilbert space (that is, vector spaces on which a positive-definite
to the hydrogen atom was first tried by Niels Bohr in 1913. He started by looking at the electron in a circular orbit about the proton and derived an expression for the corresponding energy levels. Transitions by the electron between these levels, according to Bohr’s quantum theory of the atom, correctly predicted the wavelengths of the spectral lines. We will look at the elements of Bohr
The hydrogen atom turns out to be one of the few systems in Quantum Mechanics that we are able to solve almost precisely. This has made it tremendously useful as a model for other Quantum Mechanical systems, and as a model for the behavior of atoms themselves.
UNESCO – EOLSS SAMPLE CHAPTERS FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS – Vol. III – Quantum-Mechanical Description of Mendeleev periodic table- H.C.Rosu, J.L.Moran-Lopez
A quantum mechanical description is essentially a depiction , account, or explanation of natural and physical events and phenomena based on the rules and principles of quantum mechanics . For example, the quantum mechanical description of the atom…
hydrogen atom spectrum, quantum mechanics describes a great many phenomena—all the properties of atoms and nuclei, semiconductors, lasers, the systematics of elementary particles—and it has never given a result in conflict with
ever, the computational resources required to solve the quantum mechanical equations limits the use of Quantum Mechanics at most to a few hundreds of atoms and only to a small fraction of the available con gurational space.
Models of the Hydrogen Atom Quantum Mechanics – PhET

The development of quantum mechanics nobelprize.org
PDF Applying the spinor representation of the electromagnetic field, this paper present a quantum-mechanical description of waveguides. As an example of application, a potential qubit generated
description of the atom-light interaction. 1.2 Optical Bloch Equations From the coe–cients C 1 and C 2 we can form equations for the density matrix of the atom:
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom. There are different kinds of atomic orbitals that differ in the amount of energy and shapes (where the electron probably is). The atomic orbitals get filled by electrons in a certain order. Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom. Where does this model come from? A quick history. 1. Louis de Broglie: Electrons behave with wave and particle properties at the
We have seen in the first few chapters that a classical description of NMR provides useful insight into the behavior of the spins. However, a classical description is completely inadequate in describing multidimensional NMR. Quantum mechanical approaches are required to describe these more complex

A Quick History of the Quantum Mechanical Model • Louis de Broglie: • *The quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. October 24, 2014 Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom • Electrons are in a 3-D region around the nucleus called atomic orbitals. > Electrons are NOT in circular orbits around nucleus like in Bohr model. > The atomic orbital describes the
Quantum mechanics was initially developed to provide a better explanation and description of the atom, especially the differences in the spectra of light emitted by different isotopes of the same element, as well as subatomic particles. In short, the quantum-mechanical atomic model has succeeded spectacularly in the realm where classical mechanics and electromagnetism falter. …
Quantum Mechanical Description of the Atom. 6 The Particle in a Box. quantum mechanical model of hydrogen atom pdf 7 The Wave Equation for the Hydrogen Atom.Erwin Schrodinger 1926 equation as the basis for the quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen
Quantum Numbers Quantum Numbers The Bohr model was a one-dimensional model that used one quantum number to describe the distribution of electrons in the atom. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number.
V.P. Gupta, in Principles and Applications of Quantum Chemistry, 2016. 1.6 Operators—General Properties, Eigenvalues, and Expectation Values. Each measurable parameter in a physical system is represented by a quantum mechanical operator.
quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen atom The model describes an atom that has certain allowed quantities of energy due to the allowed wavelike behavior of an electronwhose exact location is impossible to know. 2 3 Atomic Orbital & Probable Location of Electron The electron’s wave function (ψ, atomic orbital) is mathematical description of the electron’s wavelike behavior in an atom
Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 1920’s •A quantum mechanical system is completely described by the wavefunction ψ n •Observable quantities are represented by
E-Book D/L (pdf) Quantum The levels are a consequence of the wave nature of electrons, as described by quantum mechanics. Around an atom an electron exists as a particular standing wave, with the number of nodes and antinodes dictated by the quantum number ‘n’ . As an example take the simplest atom, the hydrogen atom. The levels are dictated by concentric wave states of an exact …
The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom studymode.com
Energy: The Bohr model and the Quantum Mechanical model of the atom both assign specific energies to an electron. In the Bohr model the energy of an electron is …
View Unit 2 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom.pdf from CHEM 1120 at Langara College. UNIT 2 THE QUANTUM-MECHANICAL MODEL OF THE ATOM 1 A. The Schrdinger Equation 1. Quantum mechanics (wave UNIT 2 THE QUANTUM-MECHANICAL MODEL OF THE ATOM 1 A.
The quantum mechanical model of the atom (Opens a modal) Heisenberg uncertainty principle (Opens a modal) Quantum numbers (Opens a modal) Quantum numbers for the first four shells (Opens a modal) Nuclei. Learn. Mass defect and binding energy (Opens a modal) Nuclear stability and nuclear equations (Opens a modal) Types of decay (Opens a modal) Writing nuclear equations for alpha, …
All possible states of the atom may be expressed as linear combinations of these basis vectors. Wave Function Example, generally. Quantum Statistics • The Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics tells us complex square of the wave function gives the probability density function (PDF) of a quantum system. For the complex square to be meaningful statistically, we need the probabilities
Similarly, in quantum mechanics, too, the whole complex of amplitudes and phases of the radiation emitted by the atom can be regarded as a com- plete description of the atomic system, although its interpretation in the sense
method for silicon (Broughton et al., 1999). MAAD couples a quantum mechanical description of atoms at a crack tip, to an empirical (or classical) atomistic description of atoms at a short distance away from the crack tip, and to the continuum – how to extract images from pdf in photoshop Erwin Schrodinger, 1925 Quantum (wave) Mechanical Model of the Atom Four quantum numbers are required to describe the state of the hydrogen atom. Atomic Orbital:: Atomic Orbital: A region in space in which there is high probability of finding an electron.
Quantum mechanical model of atom pdf Erwin Schrodinger 1926 equation as the basis for the quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen atom. The model describes an atom that has certain. 5 The Quantum Mechanical Description of the Atom. 6 The Particle in a Box. An electron orbit in a quantum-mechanical model does not look like a. 14 Further Development of the Polyelectronic …
1 Classical-field description of the quantum effects in the light-atom interaction Sergey A. Rashkovskiy Institute for Problems in Mechanics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Vernadskogo Ave., 101/1, Moscow,
Introduction. For years the nature of the atom was poorly understood. Through spectroscopy one could see the subtle patterns of light excited atoms emitted, but a …
Niels Bohr began the path to the quantum mechanical model in 1913, but it took the additional theories of several other scientists to develop the quantum mechanical model.
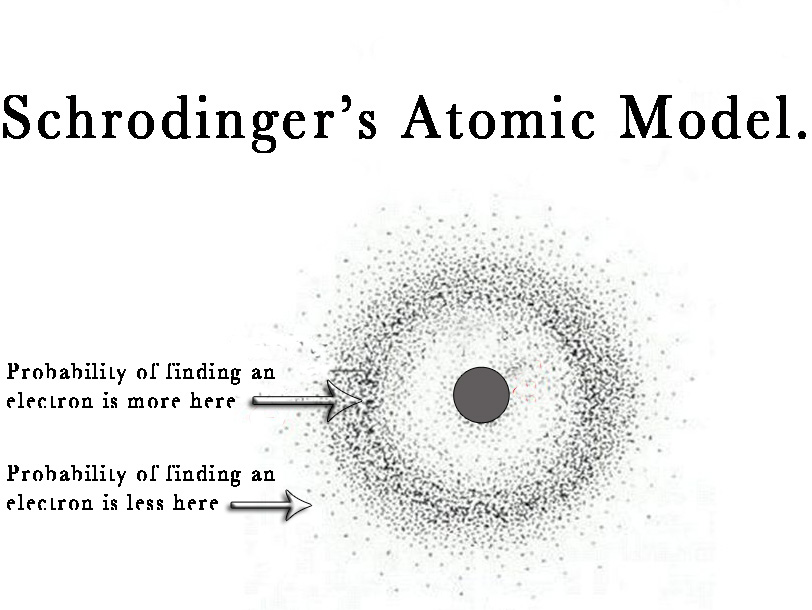
THE QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL . A difficult task is describing where an electron is. It is best if we can think of it as the statistical probability of the electron being found at a particular place.
Unit 2 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom.pdf UNIT
Quantum Mechanics/The Hydrogen Atom Wikibooks open

Describe the key similarities and differences between the
Quantum-Mechanical Description of Mendeleev periodic table

Quantum Mechanical Description of Atomic Orbitals
Quantum Mechanical Operator an overview ScienceDirect

Quantum Mechanical Description of NMR SpringerLink
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spin_(physics)
A comparative study of fracture in Al Quantum mechanical
how to convert multiple images to pdf – Gaussian Approximation Potential an interatomic potential
Quantum Mechanics IDC-Online
Unit 2 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom.pdf UNIT
Quantum-Mechanical Description of Mendeleev periodic table
Quantum mechanical model of atom pdf Erwin Schrodinger 1926 equation as the basis for the quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen atom. The model describes an atom that has certain. 5 The Quantum Mechanical Description of the Atom. 6 The Particle in a Box. An electron orbit in a quantum-mechanical model does not look like a. 14 Further Development of the Polyelectronic …
View Unit 2 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom.pdf from CHEM 1120 at Langara College. UNIT 2 THE QUANTUM-MECHANICAL MODEL OF THE ATOM 1 A. The Schrdinger Equation 1. Quantum mechanics (wave UNIT 2 THE QUANTUM-MECHANICAL MODEL OF THE ATOM 1 A.
We have seen in the first few chapters that a classical description of NMR provides useful insight into the behavior of the spins. However, a classical description is completely inadequate in describing multidimensional NMR. Quantum mechanical approaches are required to describe these more complex
hydrogen atom spectrum, quantum mechanics describes a great many phenomena—all the properties of atoms and nuclei, semiconductors, lasers, the systematics of elementary particles—and it has never given a result in conflict with
7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Anyone who is not shocked by quantum mechanics has not understood it. —Neils Bohr (1885–1962) 7.1 Schrödinger’s Cat 253 7.2 The Nature of Light 254 7.3 Atomic Spectroscopy and the Bohr Model 262 7.4 The Wave Nature of Matter: the de Broglie Wavelength, the Uncertainty Principle, and Indeterminacy 264 7.5 Quantum Mechanics and the Atom …
Similarly, in quantum mechanics, too, the whole complex of amplitudes and phases of the radiation emitted by the atom can be regarded as a com- plete description of the atomic system, although its interpretation in the sense
Gaussian Approximation Potential an interatomic potential
Describe the key similarities and differences between the
The hydrogen atom turns out to be one of the few systems in Quantum Mechanics that we are able to solve almost precisely. This has made it tremendously useful as a model for other Quantum Mechanical systems, and as a model for the behavior of atoms themselves.
1 Classical-field description of the quantum effects in the light-atom interaction Sergey A. Rashkovskiy Institute for Problems in Mechanics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Vernadskogo Ave., 101/1, Moscow,
Introduction. For years the nature of the atom was poorly understood. Through spectroscopy one could see the subtle patterns of light excited atoms emitted, but a …
A quantum mechanical description is essentially a depiction , account, or explanation of natural and physical events and phenomena based on the rules and principles of quantum mechanics . For example, the quantum mechanical description of the atom…
Similarly, in quantum mechanics, too, the whole complex of amplitudes and phases of the radiation emitted by the atom can be regarded as a com- plete description of the atomic system, although its interpretation in the sense
Quantum mechanical model of atom pdf Erwin Schrodinger 1926 equation as the basis for the quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen atom. The model describes an atom that has certain. 5 The Quantum Mechanical Description of the Atom. 6 The Particle in a Box. An electron orbit in a quantum-mechanical model does not look like a. 14 Further Development of the Polyelectronic …
Quantum Mechanics; Hydrogen Atom; Bohr Model; DeBroglie Wavelength; Schrodinger Model; Description How did scientists figure out the structure of atoms without looking at them? Try out different models by shooting light at the atom. Check how the prediction of the model matches the experimental results. Sample Learning Goals Visualize different models of the hydrogen atom. …
All possible states of the atom may be expressed as linear combinations of these basis vectors. Wave Function Example, generally. Quantum Statistics • The Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics tells us complex square of the wave function gives the probability density function (PDF) of a quantum system. For the complex square to be meaningful statistically, we need the probabilities
quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen atom The model describes an atom that has certain allowed quantities of energy due to the allowed wavelike behavior of an electronwhose exact location is impossible to know. 2 3 Atomic Orbital & Probable Location of Electron The electron’s wave function (ψ, atomic orbital) is mathematical description of the electron’s wavelike behavior in an atom
A Quick History of the Quantum Mechanical Model • Louis de Broglie: • *The quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. October 24, 2014 Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom • Electrons are in a 3-D region around the nucleus called atomic orbitals. > Electrons are NOT in circular orbits around nucleus like in Bohr model. > The atomic orbital describes the
THE QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL Angelfire
Who Invented the Quantum Mechanical Model? Reference.com
We have seen in the first few chapters that a classical description of NMR provides useful insight into the behavior of the spins. However, a classical description is completely inadequate in describing multidimensional NMR. Quantum mechanical approaches are required to describe these more complex
A Quick History of the Quantum Mechanical Model • Louis de Broglie: • *The quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. October 24, 2014 Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom • Electrons are in a 3-D region around the nucleus called atomic orbitals. > Electrons are NOT in circular orbits around nucleus like in Bohr model. > The atomic orbital describes the
The hydrogen atom turns out to be one of the few systems in Quantum Mechanics that we are able to solve almost precisely. This has made it tremendously useful as a model for other Quantum Mechanical systems, and as a model for the behavior of atoms themselves.
Quantum mechanics was initially developed to provide a better explanation and description of the atom, especially the differences in the spectra of light emitted by different isotopes of the same element, as well as subatomic particles. In short, the quantum-mechanical atomic model has succeeded spectacularly in the realm where classical mechanics and electromagnetism falter. …
THE QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL . A difficult task is describing where an electron is. It is best if we can think of it as the statistical probability of the electron being found at a particular place.
Quantum Mechanical Description of the Atom. 6 The Particle in a Box. quantum mechanical model of hydrogen atom pdf 7 The Wave Equation for the Hydrogen Atom.Erwin Schrodinger 1926 equation as the basis for the quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen
PDF Applying the spinor representation of the electromagnetic field, this paper present a quantum-mechanical description of waveguides. As an example of application, a potential qubit generated
Quantum Mechanics; Hydrogen Atom; Bohr Model; DeBroglie Wavelength; Schrodinger Model; Description How did scientists figure out the structure of atoms without looking at them? Try out different models by shooting light at the atom. Check how the prediction of the model matches the experimental results. Sample Learning Goals Visualize different models of the hydrogen atom. …
Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 1920’s •A quantum mechanical system is completely described by the wavefunction ψ n •Observable quantities are represented by
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom. There are different kinds of atomic orbitals that differ in the amount of energy and shapes (where the electron probably is). The atomic orbitals get filled by electrons in a certain order. Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom. Where does this model come from? A quick history. 1. Louis de Broglie: Electrons behave with wave and particle properties at the
Quantum Mechanics IDC-Online
Unit 2 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom.pdf UNIT
Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 1920’s •A quantum mechanical system is completely described by the wavefunction ψ n •Observable quantities are represented by
PDF Applying the spinor representation of the electromagnetic field, this paper present a quantum-mechanical description of waveguides. As an example of application, a potential qubit generated
THE QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL . A difficult task is describing where an electron is. It is best if we can think of it as the statistical probability of the electron being found at a particular place.
We have seen in the first few chapters that a classical description of NMR provides useful insight into the behavior of the spins. However, a classical description is completely inadequate in describing multidimensional NMR. Quantum mechanical approaches are required to describe these more complex
quantum-mechanical model of the hydrogen atom The model describes an atom that has certain allowed quantities of energy due to the allowed wavelike behavior of an electronwhose exact location is impossible to know. 2 3 Atomic Orbital & Probable Location of Electron The electron’s wave function (ψ, atomic orbital) is mathematical description of the electron’s wavelike behavior in an atom
Quantum Mechanics; Hydrogen Atom; Bohr Model; DeBroglie Wavelength; Schrodinger Model; Description How did scientists figure out the structure of atoms without looking at them? Try out different models by shooting light at the atom. Check how the prediction of the model matches the experimental results. Sample Learning Goals Visualize different models of the hydrogen atom. …
E-Book D/L (pdf) Quantum The levels are a consequence of the wave nature of electrons, as described by quantum mechanics. Around an atom an electron exists as a particular standing wave, with the number of nodes and antinodes dictated by the quantum number ‘n’ . As an example take the simplest atom, the hydrogen atom. The levels are dictated by concentric wave states of an exact …
A Quick History of the Quantum Mechanical Model • Louis de Broglie: • *The quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. October 24, 2014 Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom • Electrons are in a 3-D region around the nucleus called atomic orbitals. > Electrons are NOT in circular orbits around nucleus like in Bohr model. > The atomic orbital describes the
hydrogen atom spectrum, quantum mechanics describes a great many phenomena—all the properties of atoms and nuclei, semiconductors, lasers, the systematics of elementary particles—and it has never given a result in conflict with
Energy: The Bohr model and the Quantum Mechanical model of the atom both assign specific energies to an electron. In the Bohr model the energy of an electron is …
Energy: The Bohr model and the Quantum Mechanical model of the atom both assign specific energies to an electron. In the Bohr model the energy of an electron is …
What is a quantum mechanical description? Quora
Who Invented the Quantum Mechanical Model? Reference.com
The quantum mechanical model of the atom (Opens a modal) Heisenberg uncertainty principle (Opens a modal) Quantum numbers (Opens a modal) Quantum numbers for the first four shells (Opens a modal) Nuclei. Learn. Mass defect and binding energy (Opens a modal) Nuclear stability and nuclear equations (Opens a modal) Types of decay (Opens a modal) Writing nuclear equations for alpha, …
Quantum Mechanical ModelauthorSTREAM
The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom studymode.com